The Senegal 2050 plan aims to address the weaknesses in the economy and position the West African nation as a diverse and dynamic economy in the coming decades. Central to this plan is a commitment to green energy and infrastructure development. The strategy also includes significant improvements in healthcare, ensuring that a healthier population drives productivity and innovation.
Senegal’s economy is among the strongest in the Sub-region
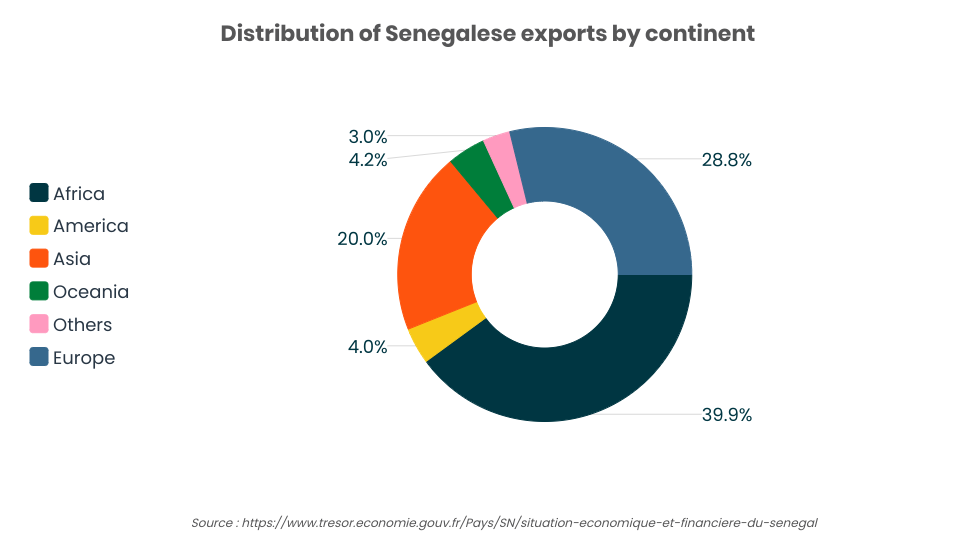
Over the past decade, Senegal’s economy has remained robust, supported by key sectors such as agriculture, mining, and services. The country’s GDP growth has consistently outperformed regional averages.
Infrastructure projects, improved business regulations, and strong regional trade relationships are some of the pillars contributing to Senegal’s stable GDP. As a member of the West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU), Senegal also benefits from a stable currency backed by the euro, helping to control inflation and provide a reliable investment environment.
Like many African countries, Senegal faces challenges related to poverty, inequality, and the need to diversify its industrial base. Traditionally, its economic expansion has relied on the primary sector, with modest manufacturing and limited participation in the global digital economy.
Senegal 2050 plan : Internal resources and human capital
As the global economy shifts toward sustainable growth and transformation, African countries are making bold decisions to shape their future economies. The Senegalese government has unveiled a comprehensive development plan that aims to drive economic transformation. The Senegal 2050 plan seeks to address the economy’s weaknesses and position the country as a diverse and dynamic economy in the coming decades.
This 25-year project aims to move Senegal away from dependence on foreign aid and debt towards a local economy focused on resources and human capital. It forms part of a radical reform promised by President Bassirou Diomaye Faye, who aims to raise the country’s living standards amid rising living costs and high unemployment.
President Faye and Prime Minister Ousmane Sonko launched this ambitious program just over a month before the anticipated legislative elections on November 17. The long-term strategy is built around several key pillars aimed at :
- Promoting inclusive and sustainable growth
- Transforming the country’s economic structure
- Elevating Senegal’s status in the global economy
Sustainable development and infrastructure
At the heart of the Senegal 2050 plan is a commitment to green energy and infrastructure development. Leveraging its vast solar, wind, and hydroelectric energy resources, Senegal is on track to become a leader in renewable energy in West Africa. The country’s substantial investments in critical infrastructure are expected to be key drivers of industrial growth and regional economic integration.
These initiatives should reduce the country’s reliance on fossil fuels, expand its industrial scope, create job opportunities, and strengthen trade links. These areas are highly promising for the investor community, especially through public-private partnerships that support the country’s development goals.
Investment in human capital
The Senegal 2050 plan prioritizes human capital, recognizing that the country’s economic future depends on the skills, education, and health of its population. Senegal aims to develop a competitive workforce capable of thriving in a modern economy by investing in educational reforms, particularly in STEM fields.
Additionally, the strategy outlines significant improvements in healthcare, ensuring that a healthier population boosts productivity and innovation. This focus on human capital positions Senegal as an attractive destination for companies seeking a skilled and growing workforce.
Digital economy and technological innovation
The development of the digital economy is another pillar of the Senegal 2050 plan. Building on a young population and increasing internet access, Senegal views digital transformation as a catalyst for innovation across various sectors. The strategy emphasizes investment in technological infrastructure, fintech, and e-commerce, aiming to position Senegal as a hub for technological innovation in the region.
For financial stakeholders, the rise of the digital economy opens up new investment opportunities, particularly in fintech, telecommunications, and digital financial services. The rapid adoption of mobile payments and online banking across West Africa reveals the vast potential that Senegal could harness by 2050.
Inclusive economic transformation
Ensuring that economic growth benefits all segments of society is a crucial aspect of the 2050 plan. The government is committed to implementing social initiatives to reduce poverty, achieve gender equality, and address income disparities.
The focus on inclusion is not just a social obligation; it is the cornerstone of sustainable economic stability. A more equitable society, with broader access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, fosters a stronger economy.
Opportunities for businesses and financial actors
The Senegal 2050 plan presents numerous opportunities for financial professionals and investors across sectors such as infrastructure, renewable energy, technology, and human capital development. The government’s emphasis on public-private partnerships creates a conducive environment for foreign direct investment.
Moreover, policies aimed at easing business practices and regulatory reforms are expected to attract international investors. Such initiatives should allow Senegal to further integrate into regional and global supply chains, positioning it as a strategic entry point for companies looking to penetrate the West African market.
Challenges facing the Senegal 2050 Plan
Despite its ambition, the 2050 plan comes with challenges. Global economic fluctuations and climate change are significant risks that could affect Senegal’s trajectory. Managing these risks prudently is essential to maintaining resilience in the face of external shocks.
Moreover, the plan’s success depends on effective implementation, which requires strong governance and collaboration between the public and private sectors. Transparency and good governance remain critical to maintaining investor confidence.